The TMJ (temporomandibular joint), functioning as a sliding hinge that connects the jawbone to the skull, can lead to discomfort and pain in the jaw joint and associated muscles.
What is the temporomandibular joint?
The two joints that attach your lower jaw to your skull are temporomandibular joints (TMJ). More precisely, these are the mandible (lower jaw) and temporal bone (side and base of the skull) joints that move and rotate in front of each ear. Among the body’s most intricate joints are the TMJs. The mandible may move forward and backward, up and down, and side to side thanks to these joints and several muscles. Chewing, talking, yawning, and swallowing are examples of smooth muscle movements that can occur when the mandible and its joints are in a balanced position. Many issues can arise when these structures—muscles, ligaments, disk, jaw, and temporal bone—are not synced or aligned in their movements.
What are TMJ disorders?
TMJ disorders are ailments that directly impact the temporomandibular joint. They can manifest in diverse symptoms, leading to varying degrees of discomfort for individuals affected.
While the majority of TMJ disorder cases resolve within a short span, usually a couple of months, some cases may persist or recur over time.
TMJ Symptoms
Symptoms associated with TMJ disorders consist of:
- Jaw pain or tenderness
- Discomfort in one or both temporomandibular joints
- Pain in the vicinity of the ear
- Challenges while chewing or pain during chewing
- Ache in the facial region
- Difficulty opening or closing the mouth due to joint locking
- Clicking or grating sensation during mouth movements
However, it’s important to note that if jaw clicking occurs without any pain or restricted movement, it might not necessitate treatment for a TMJ disorder.
What causes TMJ disorders?
Identifying the specific cause of an individual’s TMJ disorder can be challenging. Some individuals with jaw pain may also display habits such as teeth clenching, grinding, or gnashing, known as bruxism. Bruxism can manifest subconsciously during sleep or consciously during waking hours. Severe cases of bruxism can cause migraines, damage to teeth, and problems with the jaw, although minor ones might not need treatment.
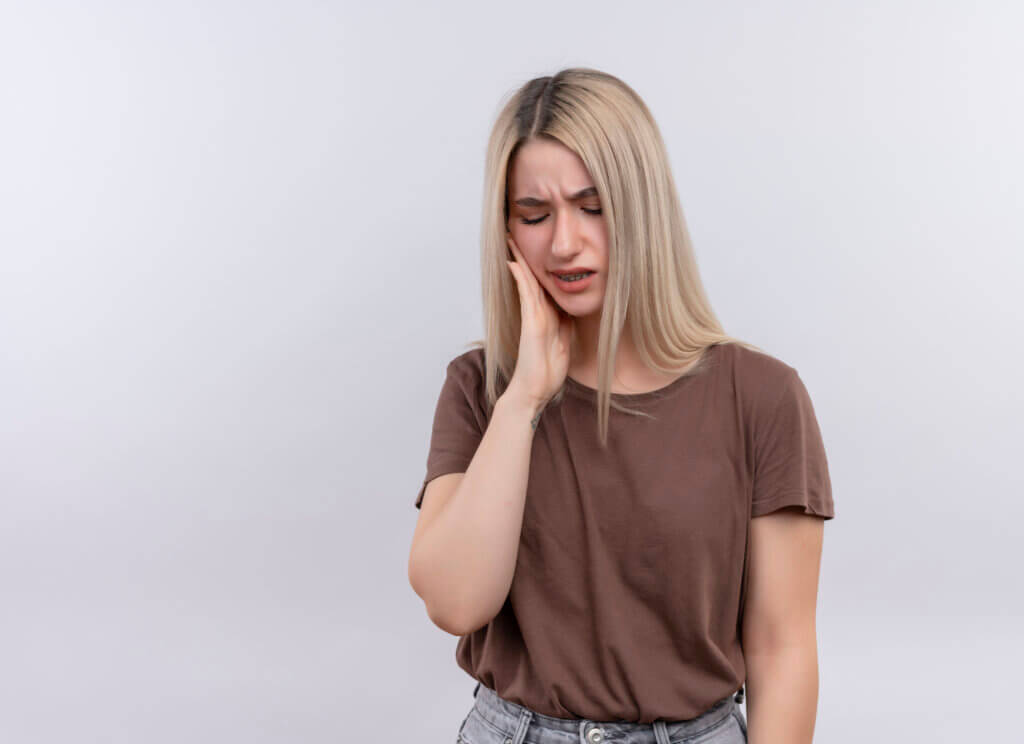

The joint that combines sliding and hinge motions is the temporomandibular joint. The cartilage covering the joint surfaces is separated from one another by a tiny cartilage disc that absorbs shock, keeping movement smooth in most cases. TMJ problems can occasionally result from a cartilage disc that has moved out of place.
Other potential causes of TMJ disorders include:
- Dislocation or damage to the disc
- Connective tissue disorders impacting the temporomandibular joint
- Injury to the joint from impacts or blows
- Inherent anatomical irregularities of the TMJ from birth (genetic predisposition)
- Deterioration of the joint’s cartilage lining due to various forms of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or inflammatory arthritis
What are the treatment options for TMJ?
In the majority of cases, approximately 95%, the pain and discomfort linked to TMJ disorders are temporary and can be alleviated through self-managed care or non-surgical interventions. These interventions encompass medication, physical therapy, and modifications to one’s lifestyle.
In most cases, surgery is viewed as a last resort when all other methods have failed. However, for those suffering from TMJ disorders, surgery may be a viable option for finding relief. Non-invasive treatments comprise:
- Limiting jaw movements to a comfortable range during rest to maintain a gap between the upper and lower teeth.
- Following a diet of soft foods to avoid exacerbating pain, opting for pureed or softened food options.
- Taking medications to alleviate jaw discomfort and relax muscles, such as muscle relaxants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or specific antidepressants.
- Applying heat or cold packs directly to the affected area to relieve pain.
- Engaging in TMJ physiotherapy, which may include acupuncture, relaxation techniques, posture correction, neck therapy, TMJ joint mobilization, adjustments to TMJ movement patterns and timing, as well as TMJ stabilization exercises.
- Using an occlusal splint or mouth guard to reduce jaw clenching or teeth grinding, particularly during nighttime.
Can you fix TMJ without surgery?
Your dentist might recommend physical treatment targeted at the jaw area, alongside orthodontic solutions like braces, jaw splints, or Temporomandibular joint retainers if your jaw issues stem from misalignment. By aligning your teeth for a more comfortable bite, these procedures can alleviate your discomfort.
In the process of rectifying your bite, TMJ treatment often involves starting with personalized self-care exercises or utilizing a custom-made mouth appliance known as an orthotic.
Can TMJ be cured by surgery?
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ), situated at the junction of the jawbone and skull, functions as a hinge-like mechanism, facilitating the vertical movement of the jaw for activities like speaking and chewing.
When affected by a TMJ disorder, individuals may experience symptoms like pain, stiffness, or limited mobility in the TMJ, hindering the complete range of motion of the jaw.
If non-invasive treatments like mouthguards or dental splints don’t alleviate the severity of symptoms, surgery could be recommended as a potential treatment option for TMJ disorders.
When is surgery recommended for TMJ?
If you’re experiencing persistent and intense symptoms associated with your temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and are considering surgery, it’s essential to be aware of the criteria your doctor might consider when recommending or advising against the procedure.
Your doctor might recommend TMJ surgery if:
- you consistently feel intense pain or tenderness during jaw movements.
- you have difficulty fully opening or closing your mouth.
- eating and drinking become challenging due to jaw pain or limited mobility.
- symptoms worsen progressively, despite rest or other non-surgical interventions.
- structural issues or diseases in your jaw joint have been confirmed through radiological imaging, such as an MRI.
Conversely, your doctor may advise against Temporomandibular joint surgery if:
- your TMJ symptoms aren’t severe, such as clicking or popping sounds without associated pain.
- symptoms fluctuate, indicating potential fatigue from specific activities rather than a chronic issue.
- you can fully open and close your jaw, even if you experience some pain or tenderness.
It’s crucial to consult with a dentist or oral surgeon specializing in temporomandibular disorders (TMD) to undergo a comprehensive evaluation. They will carefully assess your medical history, clinical symptoms, and imaging results to determine the most appropriate treatment, keeping surgery as a last resort if other non-surgical treatments prove ineffective.
Is bruxism and TMJ the same?
TMJ disorder, also known as TMD, and bruxism are distinct conditions that can both impact oral health and the proper functioning of the mouth. While bruxism is the grinding of teeth, TMJ issues are linked to pain and dysfunction of the muscles and joints that connect the lower jaw to the skull. Although bruxism can be a result of TMD, it can also aggravate or cause the condition of Temporomandibular Joint Disorder.
When To See a Dentist
TMJ often results in the onset of intense jaw and facial pain. While for many individuals, symptoms may appear without a specific trigger, it is crucial to seek medical attention if you encounter persistent pain or tenderness in your jaw.
Be vigilant for indicators such as continual pain or tenderness in the jaw, limited jaw movement inhibiting full mouth opening, as well as discomfort or challenges while chewing.
If you have observed any of the symptoms highlighted above, it’s advisable to consult experienced dentists and specialists in Temporomandibular joint disorders. Feel free to contact the COH Clinic at +90 (536) 934 6524 to investigate potential causes and discuss appropriate treatment options based on your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is TMJ caused by?
What is TMJ caused by?
It's often unclear what exactly causes this condition. Excessive tension on the muscles controlling speaking, swallowing, and chewing as well as the jaw joints might occasionally be the primary reason. Bruxism might be the cause of this. This refers to the uncontrollably habitual clenching or grinding of the teeth.
Can TMJ fully heal?
Can TMJ fully heal?
The specific cause of the pain initially will determine whether or not it may be fully treated. While certain TMJ conditions may be treatable, others may simply allow patients to manage their pain.
How long will TMJ last?
How long will TMJ last?
TMJ can occur at any moment and can last anywhere from two days to a few weeks. Eating soft meals and placing cool or hot packs on your face can assist in easing pain but are not a permanent solution.
Is TMJ serious?
Is TMJ serious?
Everyone is affected differently by TMJ disorder. For some, it's a passing phase that will pass in a week or two. For others, it is a chronic ailment that has a detrimental influence on their quality of life. Inform your doctor if you suffer regular jaw discomfort, face pain, headaches, or other TMJ symptoms.
Is TMJ permanent?
Is TMJ permanent?
Teeth grinding and clenching are two of the main causes of TMJ discomfort. Nonetheless, TMJ discomfort may be permanently cured with the right care as this is not an irreversible ailment. To begin with, you have to give up any habits of clenching or grinding your teeth, as well as anything that causes pressure on the joint.
What happens if TMJ is left untreated?
What happens if TMJ is left untreated?
This may cause muscular spasms, irregular muscular growth, and swelling of the facial muscles. Severe TMJ instances have the potential to permanently harm the jaw joints' bones. Occasionally, surgery is the patient's sole option in such cases.